What are canonical tags
A canonical tag (rel=”canonical”) is a piece of HTML code that specifies the primary version of duplicate, near duplicate, and similar pages. To put it another way, if you have the same or similar content available at multiple URLs, you can use canonical tags to specify which version is the main one and thus should be indexed. Duplicate content is a complicated topic, but when search engines crawl many URLs with identical (or very similar) content, it can cause several SEO issues. For starters, if search crawlers must sift through too much duplicate content, they may overlook some of your unique content. Second, large-scale duplication may dilute your ability to rank. Finally, even if your content ranks, search engines may choose the incorrect URL as the “original.” Canonicalization allows you to control duplicate content. Canonical tags are used in Search engine optimization to tell Google which version of a page you want to appear in search results, to consolidate link equity from duplicate pages, and to improve website crawling and indexing.
Learn some SEO tips for fresh websites
The canonical tag’s primary purpose is to inform search engines which page is the main, original version and which are just duplicates that look the same. In general, websites typically contain at least some duplicate pages, which display the same content but with different URLs. In these cases, Google must decide which page to index and rank – it will not use all the pages as search results because they all appear identical or very similar.
Aside from its primary function, the canonical tag also provides some significant SEO benefits:
- They combine pagerank: –
Canonical tags aid in the consolidation of link equity (PageRank) from all duplicate pages into a single main, canonical page. Duplicate pages frequently receive backlinks from a variety of external sources, including links from random websites, social media users, and so on. As a result, these pages take over some of the link equity from the main version of the page – the one you want to rank as a search result. By using canonical tags on duplicate pages, PageRank can be transferred into a single URL, improving its overall ranking in Google Search.
- They aid in the management of syndicated content: –
Canonical tags can inform search engines about which websites have the original version of the content and which simply republish it (or syndicate). Many website owners publish their content on other websites (either for promotional or other purposes). In this case, Google must determine which website is the original source of this content and should be displayed as a search result, as opposed to which websites simply promote it. Setting up canonical tags on these external websites’ aids in the resolution of this issue and promotes the original, main version of the page in Google Search.
- They help with crawling: –
Canonical tags allow search engines like Google to crawl and index pages that you want to crawl and index, rather than duplicates that should not be crawled at all. Duplicate pages waste Google’s resources and time because they are not necessary for crawling or indexing. By designating canonical pages, Google will concentrate its efforts on the most important pages, thereby saving the “crawl budget.”
How to add Canonical tags:
Adding canonical tags to your pages is simple: go to any duplicate webpage and add the rel=”canonical” tag to the page’s head> section. The canonical tag link should point to the main, original version. It is best to implement canonical tags on a page-by-page basis. However, on larger websites, this can take a significant amount of time and resources, if not be impossible. Fortunately, canonical tags can be automatically implemented by using various plugins such as Yoast SEO (for WordPress). The use of this plugin to implement canonical tags is simple:
- Select the page to be canonicalized.
- Navigate to the page’s “Advanced” section.
- Add the canonical URL to which you want to refer.
There are a few other ways to tell Google which pages are canonical:
Canonical tags can also be added to the webpage’s HTTP header. This is especially useful for non-HTML documents like PDFs, which lack a head> section where you could add a standard canonical tag. To add canonical tags to the HTTP header, navigate to your site’s.htaccess file and insert the canonical tag in the following format:
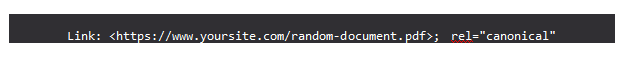
There are a few reasons why you might want to include the canonical tag in your HTTP headers. The first is to rank a PDF file’s HTML version. PDFs frequently receive many links because they are more convenient than HTML equivalents. This usually results in the PDF outranking the HTML page, which often causes issues: Analytics does not support tracking sessions to PDFs. Visitors to the PDF cannot be tagged with remarketing code. PDFs are frequently email gated; when the PDF ranks in Google, this becomes ineffective.
It is not such a difficult subject once you understand canonical tags. You can easily use canonical tags to keep your website optimised for Google’s crawlers if you follow best practises.












